Most iron flakes/prisms are produced from cast ingots for use in coating and thin film Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes.
This includes :
- Thermal and Electron Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
- Low Temperature Organic Evaporation
- Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
- Organometallic
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) for specific applications such as fuel cells and solar energy
The thickness for all metals can range from ~0.076 mm to ~2 mm. Some metals can also be rolled down as thin as 0.02 mm for use as an evaporation source in microelectronics, optics, magnetics, MEMS, and hard resistant coatings. Iron flakes are produced using crystallization, solid state and other ultra high purification processes such as sublimation.
Iron flake has several applications including but not limited to:
- Electromagnetic Coatings
- Radar Absorbing Material (RAM)1
- Magnetic Ink
- Fingerprint Detection2 and more…
You can shop for Ultrafine Iron Flakes as well as other types of flakes at our shop
-
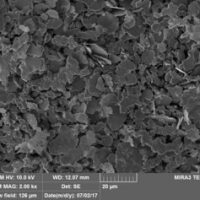 Conductive Nickel Flakes: N01$42.99 – $694.99
Conductive Nickel Flakes: N01$42.99 – $694.99 -
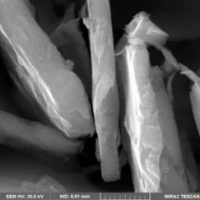 Ultrafine Iron Flake CF02$40.99 – $454.99
Ultrafine Iron Flake CF02$40.99 – $454.99 -
 Ultrafine Iron Flake CF01$39.99 – $449.99
Ultrafine Iron Flake CF01$39.99 – $449.99 -
 Bronze Flake CompositeProduct on sale$30.00 – $700.00
Bronze Flake CompositeProduct on sale$30.00 – $700.00
References
[1] Radiation-absorbent material. (2021, May 20). Retrieved June 15, 2021, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiation-absorbent_material
[2] James, J., Pounds, C., & Wilshire, B. (1993, March 01). Magnetic Flake Powders for Fingerprint Development. Retrieved June 15, 2021, from https://www.astm.org/DIGITAL_LIBRARY/JOURNALS/FORENSIC/PAGES/JFS13419J.htm
[3] American Elements. (2017, June 13). Iron Flake. Retrieved June 15, 2021, from https://www.americanelements.com/iron-flake-7439-89-6.


